Impedance Measurement
NLR has the hardware and software capabilities to assess with high detail how renewable energy devices will affect grid stability and strength.

Photo by Dennis Schroeder, National Laboratory of the Rockies
As renewable energy and power electronics proliferate on the grid, it is critical to understand how these devices will affect grid stability. But there are far too many devices and commercial varieties to assess each device analytically and individually. Instead, the industry needs a versatile and tech-agnostic approach to determine device impacts quickly and confidently.
NLR has a software tool to perform impedance scans of devices, which evaluate how renewable energy resources interact with one another and the grid at multiple timescales and for various operations. This software is compatible with any renewable energy device and can prevent early mistakes in project planning.
For renewable energy deployments that require more rigorous field validation, NLR can also plug devices into its Advanced Research on Integrated Energy Systems (ARIES) platform, which has the ability to deliver real power for custom grid scenarios and analyze the devices’ electrical response.
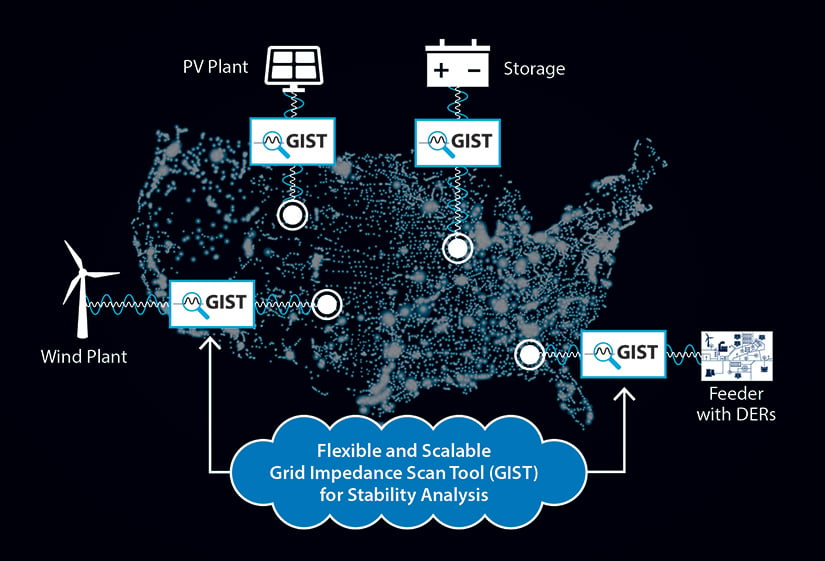
Illustration by Taylor Henry, National Laboratory of the Rockies
Software Capabilities
- Grid Impedance Scan Tool
NLR has developed the Grid Impedance Scan Tool (GIST), software to scan the impedance of any inverter-based resource (IBR), such as offshore and land-based wind power plants, solar power plants, battery energy storage systems, and high-voltage DC converter stations. GIST can scan the impedance of all types of device models (e.g., black-box, real code, and generic electromagnetic transient models) to evaluate their impact on grid stability and does not require analytical models of devices. GIST can also scan impedance of large power system networks to evaluate its stability modes. It can also be used to estimate the grid-forming capacity required or assess the stability impact of various control modes for devices. - Automated System-Wide Strength Evaluation Tool
The Automated System-Wide Strength Evaluation Tool (ASSET) analyzes system strength in terms of short-circuit ratio at the points of interconnection of inverter-based resources, considering user-defined contingencies. The tool is also capable of identifying critical N-1 and N-2 contingencies for each renewable energy plant that can result in lowest grid strength condition at the plant interconnection point. It serves as a screening tool to identify scenarios for which more comprehensive grid reliability studies are needed.
Hardware Capabilities
- Impedance measurement system
NLR has developed an in-house hardware testing system to measure impedance responses of multi-megawatt wind turbines and solar and battery inverters for characterizing their stability properties at different frequencies. The system is being used by several Department of Energy- and industry-sponsored projects to evaluate the stability impacts of wind turbine and inverter products. - Medium voltage impedance network
This hardware unit can emulate real weak grid conditions to test device-grid interactions under widely diverse scenarios, including weak grid conditions and series-compensated transmission lines. - Controllable grid interface
This hardware unit customizes power conditions for a 19-MW research bus.
Collaborations
The Australian Energy Market Operator has teamed with NLR to analyze large-scale renewable energy additions in its service territory. It has used GIST to identify the root cause of oscillations in its territory with high levels of inverter-based generation from renewables.
"GIST was able to identify the devices and controls causing the instability problems under certain operating conditions, which narrowed down the source of oscillations and enabled the Australian Energy Market Operator and network operators to explore appropriately targeted solutions with generators," said Michael Gatt, the Australian Energy Market Operator’s chief operating officer.
Presentations
Grid-Forming Inverter Hardware Testing, Energy Systems Integration Group 2024 Spring Technical Workshop (2024)
Frequency Scans for Grid-Forming Mode Performance Verification, IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (2023)
Grid Impedance Scan Tool—Software for Stability Analysis of Inverter-Based Resource Power Systems, EPRI Subsynchronous Oscillations Workshop (2023)
On the Low Risk of Subsynchronous Resonance in Type III Wind Turbines Operating in Grid-Forming Control, 21st Wind and Solar Integration Workshop (2022)
Impedance Scan Tools for Stability Analysis of Inverter-Based Resource Grids, G-PST/ESIG Webinar Series (2022)
Which IBRs Are Causing Oscillations?—A Flexible and Scalable Impedance Scan Tool To Evaluate Small-Signal Stability, Control Interactions, and Oscillations in Inverter-Based Resource Grids, NERC Inverter-Based Resource Performance Working Group (2021)
Impedance of Three-Phase Systems in DQ, Sequence, and Phasor Domains, IEEE Power and Energy Society (2020)
Publications
On the Low Risk of Subsynchronous Resonance in Type III Wind Turbines Operating With Grid-Forming Control, IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy (2024)
Grid-Forming Inverters: Project Demonstrations and Pilots, IEEE Power and Energy Magazine (2024)
A Testing Framework for Grid-Forming Resources, Power and Energy Society General Meeting (2023)
Solar PV and BESS Plant-Level Voltage Control and Interactions: Experiments and Analysis, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion (2022)
Real-World Subsynchronous Oscillations Events in Power Grids With High Penetrations of Inverter-Based Resources, IEEE Transactions on Power Systems (2022)
Reversed Impedance-Based Stability Criterion for IBR Grids, 21st Wind and Solar Integration Workshop, The Hague, Netherlands (2022)
Sequence Impedance Measurement of Utility-Scale Wind Turbines and Inverters – Reference Frame, Frequency Coupling, and MIMO/SISO Forms, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion (2022)
Impedance Methods for Analyzing Stability Impacts of Inverter-Based Resources: Stability Analysis Tools for Modern Power Systems, IEEE Electrification Magazine (2021)
Impedance-Based Prediction of Distortions Generated by Resonance in Grid-Connected Converters, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion (2019)
News
Contact
Share
Last Updated Jan. 15, 2026



