Battery Lifespan
NLR's battery lifespan researchers are developing tools to diagnose battery health, predict battery degradation, and optimize battery use and energy storage system design.
The researchers use lab evaluations, electrochemical and thermal data analysis, and multiphysics battery modeling to assess the performance and lifetime of lithium-ion battery systems to determine:
- Chemical and mechanical degradation caused by environment and cycling
- Performance, lifespan, and cost trade-offs
- Excess power, energy, and thermal management system requirements
- Warranty, second use, and other business decision factors.
NLR's modeling expertise addresses challenges in battery system design and management through diagnosis, prediction, and optimization.
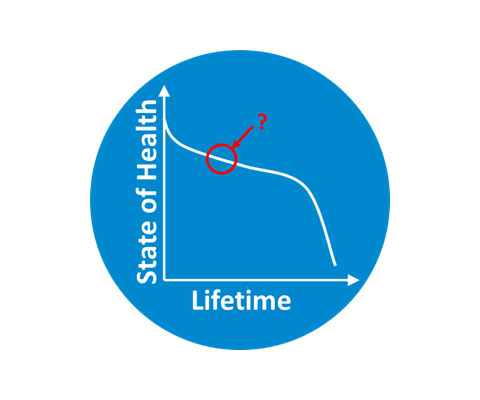
Diagnosis
Detect battery state using cheap, rapid, and scalable measurements
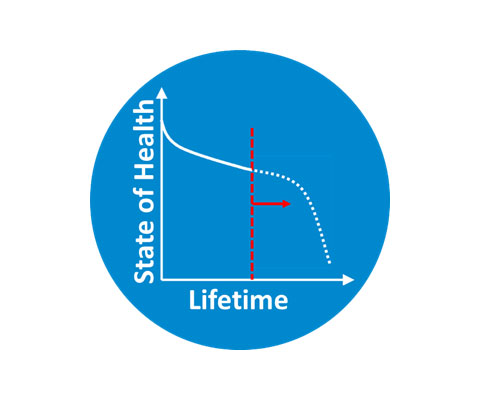
Prediction
Anticipate future battery performance by synergizing lab data and online diagnostics
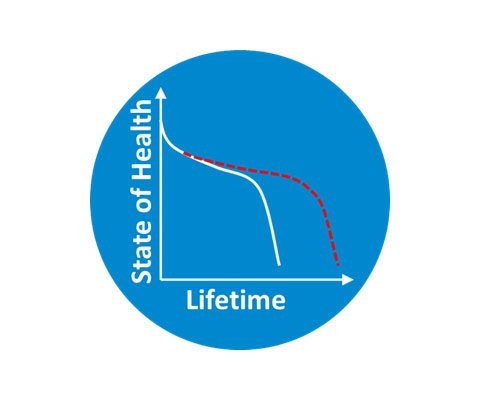
Optimization
Meet performance metrics while extending battery lifetime using predictive models and health-aware control algorithms
Battery Lifetime Diagnostics
Battery health is readily diagnosed in lab settings but can be difficult to measure during energy storage system operation, as common lab diagnostic tests require long times or expensive test equipment to perform. NLR researchers use physics-based models and machine learning to enable rapid, scalable diagnostic tests to analyze electrochemical data and monitor battery health metrics.
State-observer algorithms, such as Kalman filters, can also help estimate battery state-of-charge and state-of-health during real-world use. Using accelerated aging data, NLR developed dual-Kalman filters that update state-of-charge and state-of-health from battery voltage responses while also estimating predictive life model parameters to calculate the remaining useful life or simulate the battery degradation trajectory.
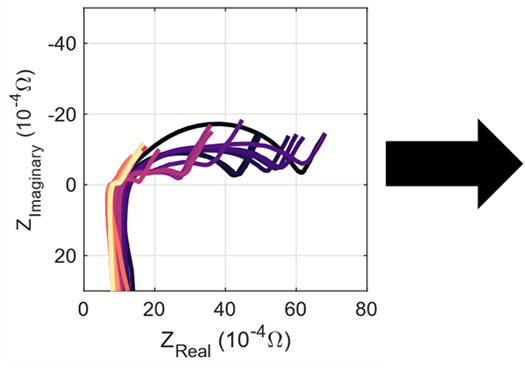
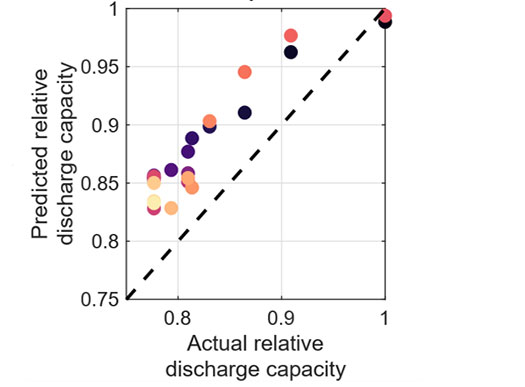
Machine-learning based prediction of battery capacity from electrochemical impedance recorded at varying temperature and state-of-charge. Image from Predicting Battery Capacity From Impedance at Varying Temperature and State of Charge Using Machine Learning, Cell Reports Physical Science (2022).
Battery Lifetime Prediction Modeling
Given that batteries degrade with use and storage, predictive models of battery lifetime must consider the variety of electrochemical, thermal, and mechanical degradation modes, such as temperature, operating windows, charge/discharge rates, storage environment, and cycling patterns. NLR uses expert insight and machine learning to identify accurate and robust models for battery life prediction with the AI-Batt tool. AI-Batt empowers rapid fitting of complex battery degradation trends with a comprehensive set of data visualization, model identification, and model simulation tools.
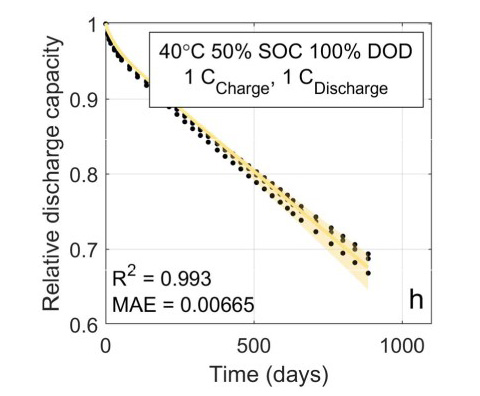
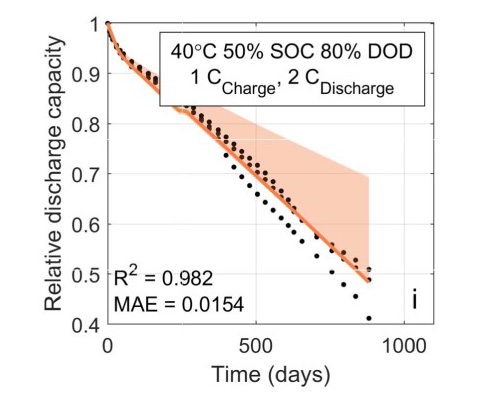
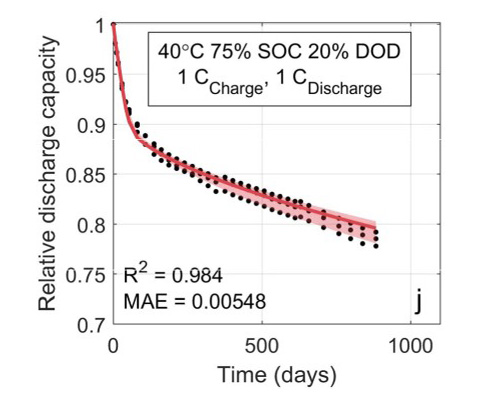
Machine-learned battery lifetime predictive model fit to experimental aging data with probabilistic lifetime estimates. Image from Machine-Learning Assisted Identification of Accurate Battery Lifetime Models With Uncertainty, Journal of The Electrochemical Society (2022).
BLAST: Battery Lifetime Analysis and Simulation Tool Suite
The BLAST suite of tools pairs NLR's high-fidelity battery degradation model with electrical and thermal performance models for modeling battery cells, packs, and systems. Open-source models for battery lifetime are provided for users to explore battery life research questions.
NLR battery life modeling capabilities include the state-of-the-art BLAST suite, extending expensive laboratory battery-aging datasets to real-world scenarios and pack architectures. The model captures degradation effects due to both calendar time and cycle aging, including constant discharge/charge cycling, as well as more complex cycling profiles, such as those found in vehicles and grid storage applications.
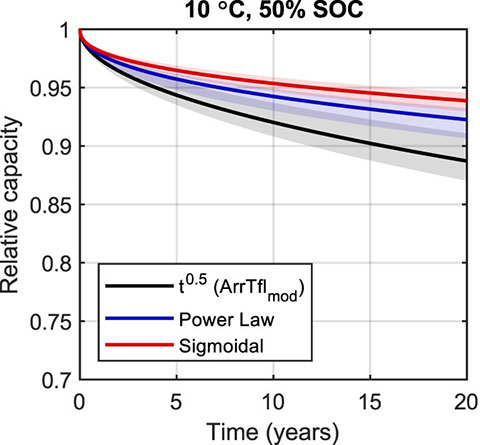
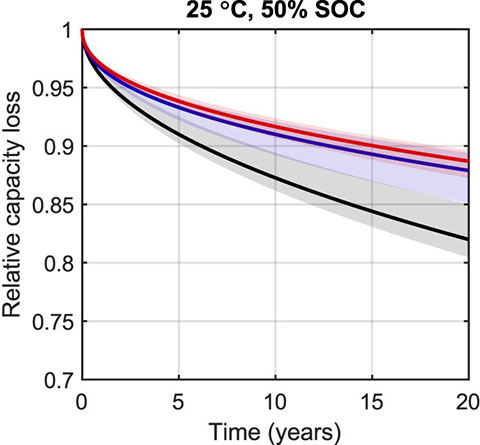
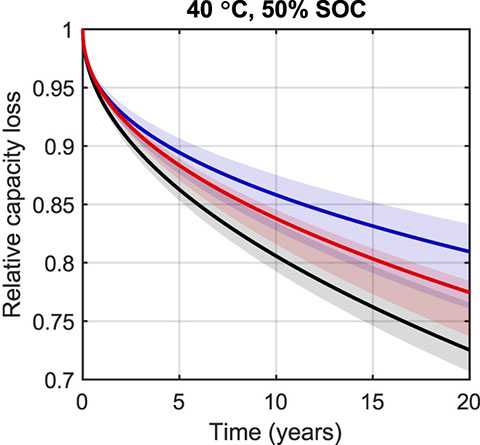
Probabilistic prediction of calendar lifetime made using various degradation models. Image from Challenging Practices of Algebraic Battery Life Models through Statistical Validation and Model Identification via Machine-Learning, Journal of The Electrochemical Society (2021).
Multiphysics models are also used to provide feedback during the cell design process. Compared to experimentation, physical models of stress and degradation allow engineers to better understand the impacts of design concepts on battery lifetime to optimize the design process. For example, multiphysics models can inform designers to reduce stresses in an electrode stack to avert a shortened lifespan, such as those caused by fast charging.
Multiphysics models of battery degradation include:
- Nonuniform degradation due to temperature and potential imbalance in large cells
- Solid/electrolyte interphase layer formation and growth
- Micro-scale and macro-scale mechanical stress and degradation, coupled with electrochemistry and temperature.
Battery Performance and Lifetime Optimization
With validated models of battery performance and lifetime, battery controls or energy storage system designs can be optimized for revenue, lifetime, or reliability. Researchers use health-aware dispatch to meet key battery performance requirements while minimizing degradation. Optimization of energy storage system design can be performed by techno-economic modeling tools, such as the Renewable Energy Integration and Optimization platform and System Advisor Model, which incorporate NLR’s predictive battery life models.
Publications
Predicting Battery Capacity From Impedance at Varying Temperature and State-of-Charge using Machine-Learning, Cell Reports Physical Science (2022)
Machine-Learning Assisted Identification of Accurate Battery Lifetime Models With Uncertainty, Journal of the Electrochemical Society (2022)
Review of ‘Knees’ in Lithium-Ion Battery Aging Trajectories, Journal of the Electrochemical Society (2022)
Lithium-Ion Battery Life Model With Electrode Cracking and Early-Life Break-In Processes, Journal of the Electrochemical Society (2021)
Analysis of Degradation in Residential Battery Energy Storage Systems for Rate-Based Use-Cases, Applied Energy (2020)
Challenging Practices of Algebraic Battery Life Models Through Statistical Validation and Model Identification via Machine-Learning, Journal of the Electrochemical Society (2021)
Life Prediction Model for Grid-Connected Li-Ion Battery Energy Storage System, American Control Conference (2017)
Contacts
Share
Last Updated Dec. 6, 2025
