Clean Energy to Communities Program Launches: Stakeholder-Informed Program Meets Communities Where They Are
Three Levels of Energy-Transition Support Address Range of Technical Needs
Local governments glimpsed a world of possibilities when the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) released its Los Angeles 100% Renewable Energy Study (LA100) in 2021. It revealed possible pathways to achieve the city’s goal of 100% renewable energy by 2045 and the implications of these pathways for the people who live and work in LA. Across the United States, communities large and small, urban and rural—or somewhere in between—need similar support: tailored solutions to help them achieve their clean energy goals at a rapid pace.
That is why the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) and NREL interviewed 164 stakeholders from 95 communities—representing 40 states and six tribes—to inform the creation of its new community technical assistance program: Clean Energy to Communities (C2C).
“We asked local government and nongovernment organizations what they needed most,” NREL Principal Investigator Jenny Sumner said. “They were asked what their most pressing energy planning questions were and how they prefer to work with the federal government.”
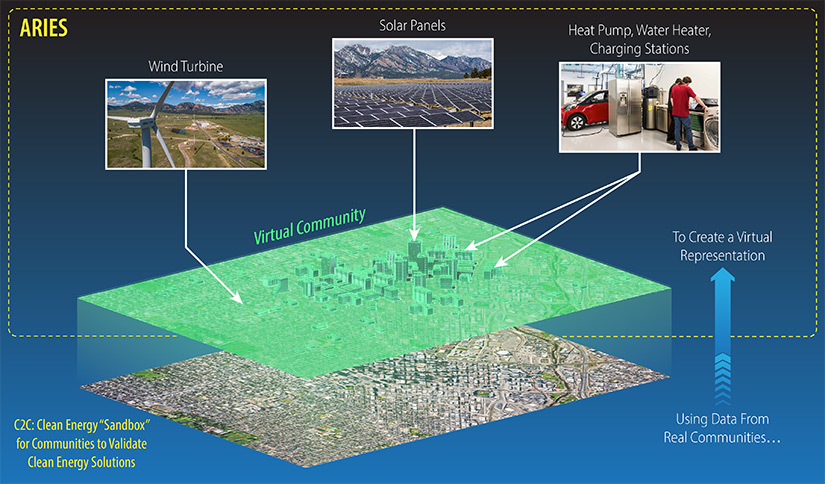
What emerged is a cross-sectoral program—spanning power, mobility, and buildings technologies—that lets local leaders see a virtual model of their community shift over time as it interacts with clean energy infrastructure and devices. This C2C program feature is made possible by NREL’s Advanced Research on Integrated Energy Systems (ARIES)—the nation's most advanced research platform for clean energy systems integration research and validation. ARIES simulates and visualizes how different clean energy technologies will impact a community’s entire energy system over a period of time. Utilities, local governments, and community-based organizations can analyze and validate their options in this virtual environment by connecting to real hardware, thereby de-risking their investment.
C2C is designed to serve a wide range of communities—from small rural communities to large urban centers; from communities just starting out on their transition to clean energy to those ready to implement—by offering multiple levels and types of technical assistance.
Meeting Communities Where They Are
“Local governments, utilities, and community-based organizations know the nuances of their communities’ energy challenges and priorities,” Sumner explained. “C2C is designed to help these stakeholders access the research and development capabilities at DOE’s national labs, including NREL, that they need to unlock practical pathways that achieve their goals.”
Integrated Energy Pathways
Integrated energy pathways modernizes our grid to support a high level of renewables, incorporates storage and advanced controls, and expands transportation electrification while maintaining grid reliability and security.
C2C connects local governments, utilities, and community-based organizations with national laboratory experts who can help them address interconnected issues. The goal is to ensure that communities have de-risked plans for meeting their advanced clean energy goals.
No matter where a community is in their energy transition, C2C can assist with goal setting and project development, all the way to validating how renewables will operate on their grids. And the program is designed to support communities that might not have all the resources or capacity typically needed to take advantage of programs like these.
“Communities are often short on resources for this level of planning. Many also want training and institutional capacity building so they can be the knowledge owners and can move forward independently,” explained Sherry Stout, NREL’s laboratory program manager for its State, Local, and Tribal program. “C2C is a program that meets communities where they are to help them take the next steps.”
Communities can participate in C2C through three levels of support: In-Depth Partnerships, Peer-Learning Cohorts, and Expert Match.
In-Depth Partnerships
For long-term support, this three-year technical partnership connects community teams of local governments, utilities, community-based groups, and others with support from national laboratory experts and their customized, cutting-edge modeling, analysis, and validation capabilities to de-risk advanced clean energy solutions.
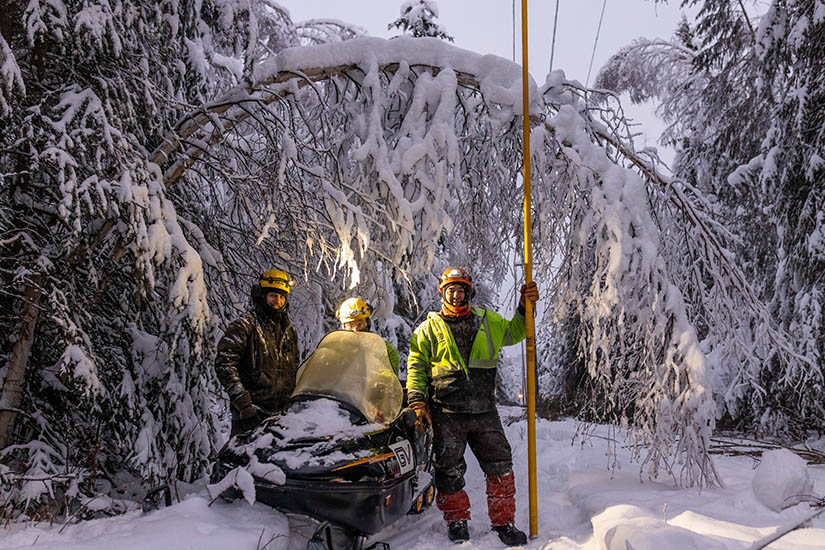
In Fairbanks, Alaska, NREL helped the local utility understand—at the operational level—the impacts of replacing its coal plant with a combination of wind and storage. NREL’s ARIES platform played a key role in validating the options. The Golden Valley Electric Association utility received production cost modeling and grid stability analysis. Leveraging the power of NREL’s 8-petaflop supercomputer, ARIES allowed researchers to emulate the community’s energy system using actual hardware and evaluate the operational feasibility of clean energy designs in its virtual environment. Read more about the Fairbanks, Alaska, C2C project.

Peer-Learning Cohorts
Communities consistently say that learning from their peers is a preferred mechanism for making progress on their clean energy ambitions. Over a six-month period, C2C’s Peer-Learning Cohorts provide communities with strategic and technical support; helpful materials, such as templates, trainings, tools, best practices, and analyses; and opportunities for collaboration with other communities across the United States facing similar challenges.
In the pilot phase of Peer-Learning Cohorts, which started in January 2023, groups of up to 15 communities are learning from national laboratory experts and from each other as they follow one of three topic areas. The topic areas will change for each cohort and are selected based on input received from the applicants about their biggest priorities. The first cohort will be exploring implementation of 100% clean energy; deployment of grid-friendly electric vehicle charging infrastructure; and clean energy financing for low-income households. Topics will vary from cohort to cohort, taking into consideration input from a broad range of communities.
Expert Match
For communities in need of shorter-term answers or facing time-sensitive decisions, Expert Match is a way to get rapid assistance from national laboratory researchers across the country. During a pilot phase of the C2C program, the city of Cohoes, New York, leveraged Expert Match to explore developing a 3.2-megawatt municipally owned and operated floating photovoltaic (FPV) solar array on its municipal reservoir—the first of its kind in the nation. The city also needed help evaluating multiple proposals to retrofit its municipal buildings to be more energy efficient, while adhering to historic preservation goals. NREL provided timely input on state policy and regulations as well as estimated FPV energy output, operations and maintenance considerations, and financing options.
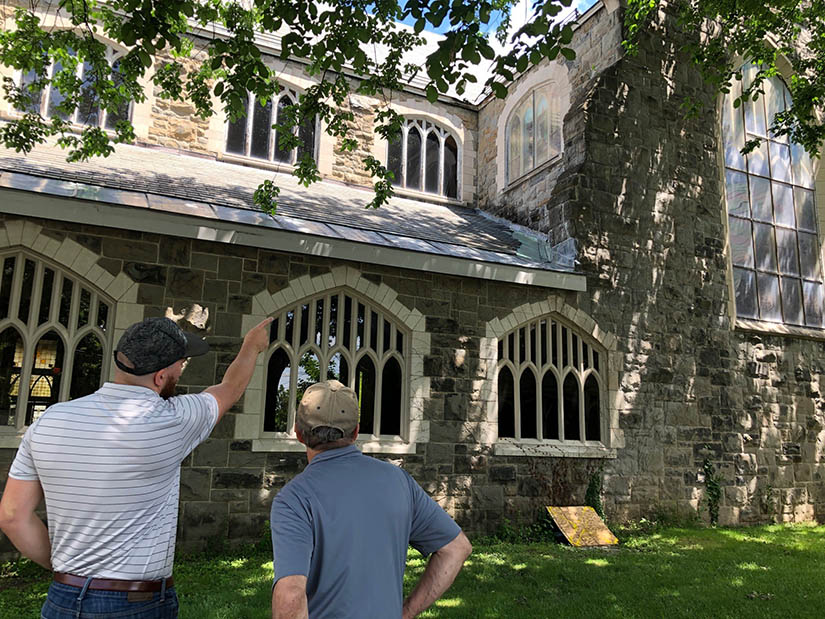

“We have a lot of the same struggles that older upstate New York communities or northeastern municipalities have, including aging infrastructure, high electricity and gas bills, and just a lack of technical expertise,” City Planner Joseph Seman-Graves said. “[Expert Match] was very valuable because it was almost a one-stop shop to get advice and technical assistance.”
The Expert Match guidance on decarbonizing historic buildings has now helped Cohoes advance its building retrofit project into the design phase for HVAC, roofing, windows, and masonry. Cohoes will also install its floating solar array on the water reservoir within the next year.
Apply To Bring Clean Energy to Your Community
Learn more about C2C including how to apply for technical assistance.
This article has been updated to reflect an editorial change made after its original publication.

