Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle Basics
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) uses a battery to power an electric motor and uses another fuel, such as gasoline or diesel, to power an internal combustion engine.
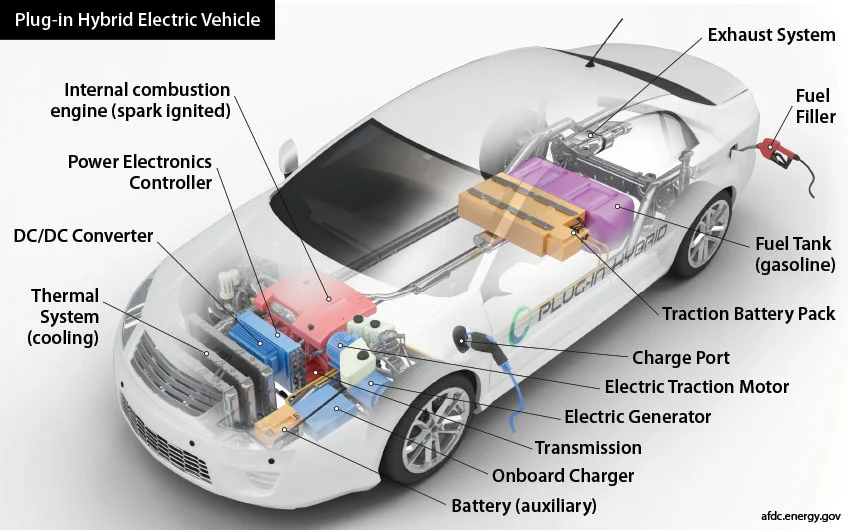
The battery pack in a PHEV is generally larger than in a standard hybrid electric vehicle. The larger battery pack allows the vehicle to operate predominantly on electricity during short trips. For longer trips, a PHEV can draw liquid fuel from its onboard tank to provide a driving range similar to that of a conventional vehicle. An onboard computer determines which fuel to use based on the mode that allows the vehicle to operate most efficiently.
The battery can be charged by plugging into an electric power source, through regenerative braking, and by the internal combustion engine. In regenerative braking, kinetic energy normally lost during braking is captured and stored in the battery.
Additional Resources
Transportation and Mobility Research
Alternative Fuels Data Center: Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (U.S. Department of Energy)
Alternative Fueling Station Locator: Electric Vehicle Charging Stations (U.S. Department of Energy)
Share
Last Updated Aug. 27, 2025
