Solar Reliability, Affordability, and Grid Flexibility: Solar Energy Innovation Network Round 1
In the first round of the Solar Energy Innovation Network (SEIN), nine teams developed new ways to improve the affordability, reliability, and resiliency of solar energy on the electric grid while moving toward ambitious solar adoption goals.
SEIN Round 1 teams received direct funding, analytical support, and facilitation support to supercharge their projects. The nine teams were grouped into two cohorts—Options Analysis and Grid Flex—based on shared challenges and goals. The Options Analysis cohort shared a focus on evaluating and experimenting with the ways solar photovoltaics (PV) could support long-term climate and energy goals. The Grid Flex cohort focused on developing and testing novel approaches to deploying solar PV in ways that would support resilience and combine solar PV with other technologies, such as electric vehicle (EV) charging. Their projects are described below.
In addition to team-level efforts, the Innovation Network produced products and tools to address questions identified by Round 1 teams, including:
- Understanding the potential impact of EVs on electricity demand
- Identifying considerations for the structure of new solar tariffs and programs
- Developing plans for moving from solar energy goals to implementation for cities and states pursuing 100% renewable energy economies
- Analyzing and compensating the locational value of solar to provide grid and resiliency benefits.
Participating Teams
This map highlights the locations of SEIN Round 1 teams and potential adopters of SEIN outputs (peer network; see below for more detail).
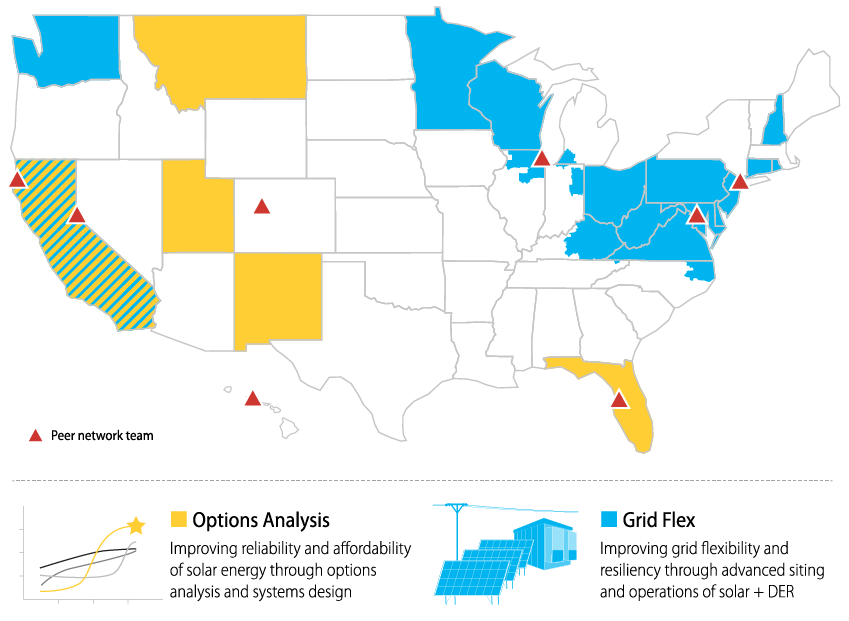
The program's first two cohorts bring together teams from across the country to address shared challenges and drive problem solving and innovation for tomorrow's electric grid.
Improving Reliability and Affordability of Renewable Energy Through Options Analysis and Systems Design Cohort
This cohort, also called "Options Analysis," focused on the role that solar PV could play in achieving high penetration goals in several different contexts. This included understanding grid impacts, planning potential pathways, and developing novel solutions to overcome barriers anticipated for high penetration levels of solar and other distributed energy resources (DERs). Activities in this cohort included:
- Developing data sets and geospatial mapping tools that assessed impacts on the reliability of various levels of variable generation at the municipal or utility service territory scale
- Identifying and validating new solar siting methods that minimized grid impacts and reduced distribution system costs
- Identifying innovative ownership models, financing structures, and procurement strategies
- Exploring options for the integrated planning and deployment of solar and EVs and solar plus storage
- Exploring alternative rate designs and compensation mechanisms.
The five project teams for this cohort are described below.
Lead Organization: City of Orlando
Team Members: City of Orlando, Orlando Utility Commission, University of Central Florida Solar Energy Center, Greenlink
The City of Orlando determined approaches to increase solar and solar-plus-storage deployments that supported energy resiliency, environmental quality, and affordability of electricity supply. The team identified total solar potential citywide, and conducted a detailed analysis for municipal facilities and distribution grid modeling. In addition, the City of Orlando launched a pilot project to demonstrate innovative siting solutions and published insights on municipal-level solar policies and building guidelines to share with other municipalities.
States Represented: Florida
Publications:
Economics of Solar with Storage for Municipal Buildings in the City of Orlando, NLR Presentation (2019)
Lead Organization: City of San Diego
Team Members: City of San Diego, Clean Coalition, San Diego Gas & Electric (invited partner)
The City of San Diego estimated the total potential for solar deployment across the city, designed a program proposal for utilizing the total solar potential, completed a detailed economic analysis of solar options on municipal facilities, conducted stakeholder workshops to explore solar compensation options, and explored opportunities for solar plus storage to improve resiliency at critical facilities. These activities informed the development of a broader roadmap for energy technology deployment that supported the city’s targets.
States Represented: California
Publications:
Economics of Solar with Storage for Municipal Sites in the City of San Diego, NLR Presentation (2019)
Lead Organization: Montana Renewable Energy Association
Team Members: Montana Renewable Energy Association, Montana Energy Office at the Department of Environmental Quality, City of Missoula, City of Bozeman, City of Whitefish, Climate Smart Missoula, Yellowstone-Teton Clean Cities
The Montana team investigated the synergies between solar generation and EV charging, including the potential opportunities and challenges related to co-locating solar energy and charging infrastructure to reduce costs and enhance co-benefits of the electrification of transportation. The cities that participated in the program (Bozeman, Missoula, and Whitefish) held stakeholder engagement meetings to clarify goals and strengthened their relationship with the utility through continued dialogue. The City of Missoula's transit agency conducted cost-benefit analysis and REopt® optimization to understand specific options for locating charging infrastructure with solar generation for six electric buses. In addition, the team completed a roadmap for advancing EV-plus-PV deployment to share broader lessons learned with other communities across Montana and the United States.
States Represented: Montana
Publications:
Economics of Solar PV and Stationary Storage for Electric Bus Charging in Missoula, Montana, NLR Presentation (2019)
Navigating Options for Transportation Electrification and Solar Charging: Steps and Lessons Learned in Montana Communities, NLR Subcontract Report (2024)
Lead Organization: Utah Clean Energy
Team Members: Utah Clean Energy, City of Moab, Park City, Salt Lake City, Rocky Mountain Power
This team evaluated the affordability and reliability of renewable generation for Salt Lake City, Park City, and Moab, informing a roadmap to help meet the cities’ energy resiliency goals. In addition, the team estimated the potential future load associated with beneficial residential electrification and EV adoption in the cities. These analyses informed a regional energy planning process and city input to the utility integrated resource planning process.
States represented: Utah
Lead organization: Kit Carson Electric Cooperative (KCEC)
Team Members: KCEC, Guzman Energy, Renewable Taos
KCEC partnered with multiple stakeholders to deploy an additional 35 megawatts of solar PV by strategically deploying smaller one-megawatt solar arrays across their service area. In coordination with NLR, the team developed a tool to identify the benefits and impacts of solar plus storage at specific locations on the grid, conducted complex scenario analyses across an entire distribution system, and identified opportunities for infrastructure and operational cost savings and improved resilience. Using the model, the team completed an operational plan for solar build-out on their system.
States Represented: New Mexico
Improving Grid Flexibility and Resiliency Through Advanced Siting and Operations of Solar Plus DER Cohort
This cohort, also called "Grid Flex," focused on quantifying the value of combining solar and other DERs, such as storage for grid flexibility, reliability, and resiliency.
Activities for this cohort included:
- Assessing opportunities to improve PV's value through siting, load management, storage, and better integration with transportation electrification
- Evaluating options for rate structures and other compensation mechanisms to effectively
value solar-plus-DER systems' various value streams
- Exploring program and policy options to account for locational value and wholesale market participation
- Improving utility and independent system operator/regional transmission organization (ISO/RTO) planning to incorporate PV and other DERs into activities like black start
- Developing needed data sets and tools for states and ISOs to evaluate solar-plus-DER solutions for increased grid resiliency.
The four project teams that participated in this cohort are described below.
Lead Organizations: PJM Interconnection and National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC)
Team Members: NARUC, PJM Interconnection, Converge Strategies LLC
This project identified opportunities for solar to provide system resilience both at distribution and bulk power levels. This included black start functionality with solar-plus-storage systems and PV potential for demand response, frequency regulation markets, and supply energy. The team members determined market barriers and potential pathways forward with input from key stakeholders, including member utilities; relevant federal, state, and local governments; regulators, developers, solution providers, and the United States military. By exploring a concrete cast study of solar for resilience, the team assessed technical feasibility, operational challenges, and business model barriers for PV and storage that supported black start services for PJM.
States Represented: PJM territory (includes Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia), and NARUC member commissions
Publications:
The Value of Resilience for Distributed Energy Resources: An Overview of Current Analytical Practices, NARUC (2019)
Advancing Electric System Resilience with Distributed Energy Resources: A Review of State Policies, NARUC (2020)
Advancing Electric System Resilience with Distributed Energy Resources: Key Questions and Resources, NARUC (2020)
Blackstart of Power Grids with Inverter-Based Resources, NLR Conference Paper (2020)
Lead Organization: Clean Energy States Alliance
Team Members: Clean Energy States Alliance, Connecticut (Connecticut Green Bank), District of Columbia (Office of the People's Counsel for the District of Columbia), New Hampshire (New Hampshire Public Utilities Commission), Rhode Island (Rhode Island Office of Energy Resources), Washington (Washington Department of Commerce's State Energy Office), Wisconsin (Wisconsin Office of Energy Innovation)
This project explored methods to identify high-value locations for distributed solar and other DERs to reduce grid congestion, avoid or defer distribution system upgrades, and provide resiliency benefits. The team determined specific elements to analyze locational value, including compensation mechanisms, data collection to advance location siting, integrated resource planning roles, solar-plus-storage utilization to manage peak demand growth, and resilience benefits of locational siting. The team published advancements and lessons learned to assist other states facing similar opportunities and challenges.
States Represented: Connecticut, District of Columbia, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Washington, and Wisconsin
Publications:
Distributed Rate Design: A Review of Early Approaches and Practical Considerations for Value of Solar Tariffs, The Electricity Journal (2020)
State Strategies for Valuing Distributed Energy Resources in Cost-Effective Locations, Clean Energy States Alliance (2020)
Lead Organization: Great Plains Institute
Team Members: Great Plains Institute, Minnesota Department of Commerce, Minnesota Department of Administration, ZEF Energy, Metropolitan Council, Minnesota Solar Energy Industries Association, Center for Energy and Environment
This project examined synergies between EV charging infrastructure and distributed solar energy. The project assessed technical applications, potential partnerships, and opportunities for local and state policies creating mutually beneficial co-deployment of solar and EVs in Minnesota. Using stakeholder engagement and economic analysis, the Minnesota team examined market potential and barriers to deployment of solar plus EV charging. Pilot projects tested EV and solar synergies, informing the development of a roadmap for cost-effective solar and EV co-deployment while supporting grid reliability.
States Represented: Minnesota
Publications:
Evaluating Utility Costs Savings for EV Charging Infrastructure, NLR Presentation (2019)
Solar Power + Electric Vehicle Charging: Capturing Synergies in Minnesota, NLR Subcontract Report (2024)
Lead Organization: Center for Climate Protection
Team Members: Center for Climate Protection, TerraVerde Energy LLC, Lancaster Choice Energy, Peninsula Clean Energy
This project developed tools and methodologies to evaluate the opportunities and tradeoffs across various rate structures for integrated DER deployment. Design decisions were based on a multi-month stakeholder input process that included community choice aggregations, solutions providers, and regulatory policy and rate design experts. The rate design tool that resulted is technology-agnostic (e.g., it encompasses distributed solar PV, energy efficiency, energy storage, electric vehicles, and demand response technologies), allowing load-serving entities to adopt and customize it based on their community goals while maintaining affordability.
States Represented: California
Publications
Visit the SEIN publications page and filter by Round 1 to see all the publications from the first round teams.
Peer Network
The Peer Network was composed of stakeholder pursuing projects that were thematically related to SEIN Round 1 teams. The teams pursued projects described below while frequently engaging with SEIN Round 1 teams to exchange ideas and stress test approaches. Peer Network teams received assistance in adapting research, analytical pathways, and innovative approaches to their individual contexts.
The relevant efforts of the six Peer Network teams are summarized below.
Lead Organization: University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa
Stakeholders: REDLab, State of Hawaii Division of Consumer Advocacy
Relevant Efforts: The long-term objective of this team is to develop coordinated control algorithms for battery energy storage systems (BESS) to mitigate hosting capacity constraints on distribution circuits for solar PV systems.
Geographic Area Represented: Hawai'i
Lead Organization: New York Power Authority (NYPA)
Stakeholders: NYPA
Relevant Efforts: NYPA's Energy Diversity through Grid Edge (EDGE) initiative is focused on finding new and innovative ways to deliver distributed energy resources to customers. Interventions range from simple energy efficiency measures, such as LED lighting installation, to development and operation of combined solar and energy storage assets.
Geographic Area Represented: New York
Lead Organization: Clean Energy Economy for the Region (CLEER)
Stakeholders: Garfield Clean Energy (government collaborative), Eagle County, Pitkin County, Xcel Energy, Holy Cross Energy, Glenwood Springs Municipal Utility, Aspen Municipal Utility, CLEER, Community Office for Resource Efficiency (CORE)
Relevant Efforts: The Western Colorado Rural Clean Energy Corridor initiative is a collaborative team spanning three counties in western Colorado. The team was creating and implementing a shared roadmap to meet the region's renewable energy goals while maximizing resilience and local economic diversification. The effort focused on developing a regional approach to renewable energy development that meets a diverse set of economic drivers and objectives.
Geographic Areas Represented: Colorado; Garfield, Pitkin, and Eagle Counties; Communities of Parachute, Rifle, Silt, New Castle, Glenwood Springs, Carbondale, Basalt, Aspen, Snowmass Village, Eagle, Vail, Avon, Gypsum, Minturn
Lead Organization: Redwood Coast Energy Authority (RCEA)
Stakeholders: RCEA, Humboldt County Planning and Building Permitting Department, Schatz Energy Research Center, The Energy Authority
Relevant Efforts: RCEA is a community choice aggregator in Humboldt County, California that has been procuring electric power on behalf of some 60,000 customers in the county since May 2017. The RCEA team was in the process of developing a 2.1 megawatt solar PV / 2 megawatt (8 megawatt-hour) battery storage microgrid system at the local airport. In addition to technical considerations, the RCEA team is also exploring a range of market and transactional questions related to microgrid development, including how costs and benefits will be allocated across customers, potential resilience value streams, and which energy markets to participate in.
Geographic Area Represented: Humboldt County, California
Lead Organization: Extensible Energy
Stakeholders: Extensible Energy
Relevant Efforts: Extensible Energy was exploring new business models and partner ecosystems to simplify combined solar, storage, and load management solutions for commercial energy customers. These efforts complemented the team's ongoing software development and testing initiatives to enable commercial customers to maximize the use of behind-the-meter solar PV installations through a combination of energy storage and automated load flexibility solutions.
Geographic Areas Represented: California
Lead Organization: Seven Generations Ahead
Stakeholders: Village of Oak Park; Village of River Forest; Oak Park River Forest Community Foundation; Oak Park Residence Corporation; Oak Park Housing Authority; Park District of Oak Park; Seven Generations Ahead; Illinois Community Choice Aggregation Network
Relevant Efforts: The Oak Park-River Forest PlanItGreen initiative incorporated a combination of renewable energy road map planning and implementation, with an emphasis on low-to-moderate income (LMI) and non-profit procurement goals.
Geographic Areas Represented: Oak Park and River Forest, Illinois
Share
Last Updated Jan. 28, 2026
